Buildroot Environment¶
Buildroot is used to build Embedded Linux Systems that can be cross compiled for unique hardware targets such as the Altronix LinQ Master module or the Microchip Sama5D27 SOM1 Module. Buildroot has it’s own user manual and the Altronix LinQ Network User Guide is only meant as a companion guide. Users should read the Buildroot User Manual in its entirety, paying closer attention to the Section 8.5 - Building Out of tree [1], Section 8.6 - Environment Variables [2], Section 8.12 - Advanced Usage [3], Section 9 - Project specific customization [4], and Section III - developer guide [5].
Required Packages¶
If you find any packages are missing, please add them to the list by submitting a PR.
- which
- sed
- make (version 3.81 or any later)
- binutils
- build-essential (only for Debian based systems)
- gcc (version 4.8 or any later)
- g++ (version 4.8 or any later)
- bash
- patch
- gzip
- bzip2
- perl (version 5.8.7 or any later)
- tar
- cpio
- unzip
- rsync
- file (must be in /usr/bin/file)
- bc
- python (version 2.7 or any later)
- Etcher
Optional Packages¶
- asciidoc, version 8.6.3 or higher
- w3m
- python with the argparse module (automatically present in 2.7+ and 3.2+)
- dblatex (required for the pdf manual only)
- graphviz to use graph-depends and <pkg>-graph-depends
- python-matplotlib to use graph-build
Altronix Buildroot Packages¶
Buildroot offers the BR2_EXTERNAL environment variable as a convenient option to store packages outside of the mainline buildroot repository. Altronix uses this environment variable to extend buildroot with Altronix specific packages such as the LinQ Network library and application demos. To get started with buildroot, clone the altronix buildroot repository and the buildroot-external-altronix submodule into your development workspace.
git clone https://bitbucket.org/Altronix/buildroot-at91
cd buildroot-at91
git submodule update --init
You are now ready to configure and compile your embedded linux system.
Note
BR2_EXTERNAL environment variable is required to be set so that buildroot can find our custom defconfig files. For convience you can export this environment variable to your shell. Or you can choose pass this environment variable to make directly.
export BR2_EXTERNAL=./external/buildroot-external-altronix
make sama5d27_som1_ek_altronix_defconfig
# Or
make BR2_EXTERNAL=./external/buildroot-external-altronix sama5d27_som1_ek_altronix_defconfig
Altronix Demo Configuration¶
From inside your buildroot-at91 workspace you can observe the following directory structure:
buildroot-at91/
|-- arch/
|-- board/
|-- boot/
|-- configs/
|-- dl/
|-- docs/
|-- package/
| |-- ... <-- mainline buildroot packages
|-- external/
| |-- buildroot-external-altronix/
| | |-- board/
| | |-- configs/
| | | |-- sama5d27_som1_ek_headless_defconfig <-- Microchip Demo Config
| | | |-- sama5d27_som1_ek_altronix_defconfig <-- Altronix Demo Config
| | | |-- ...
| | |-- package/
| | | |-- ... <-- Extra Microchip + Altronix Packages
In order to create your own Embedded Linux System you should start from a configuration that is most similar to your target hardware and software requirements. To create. To explore the Altronix Demo Configuration, run the command from buildroot-at91 root directory:
make menuconfig
You should see the following menu.
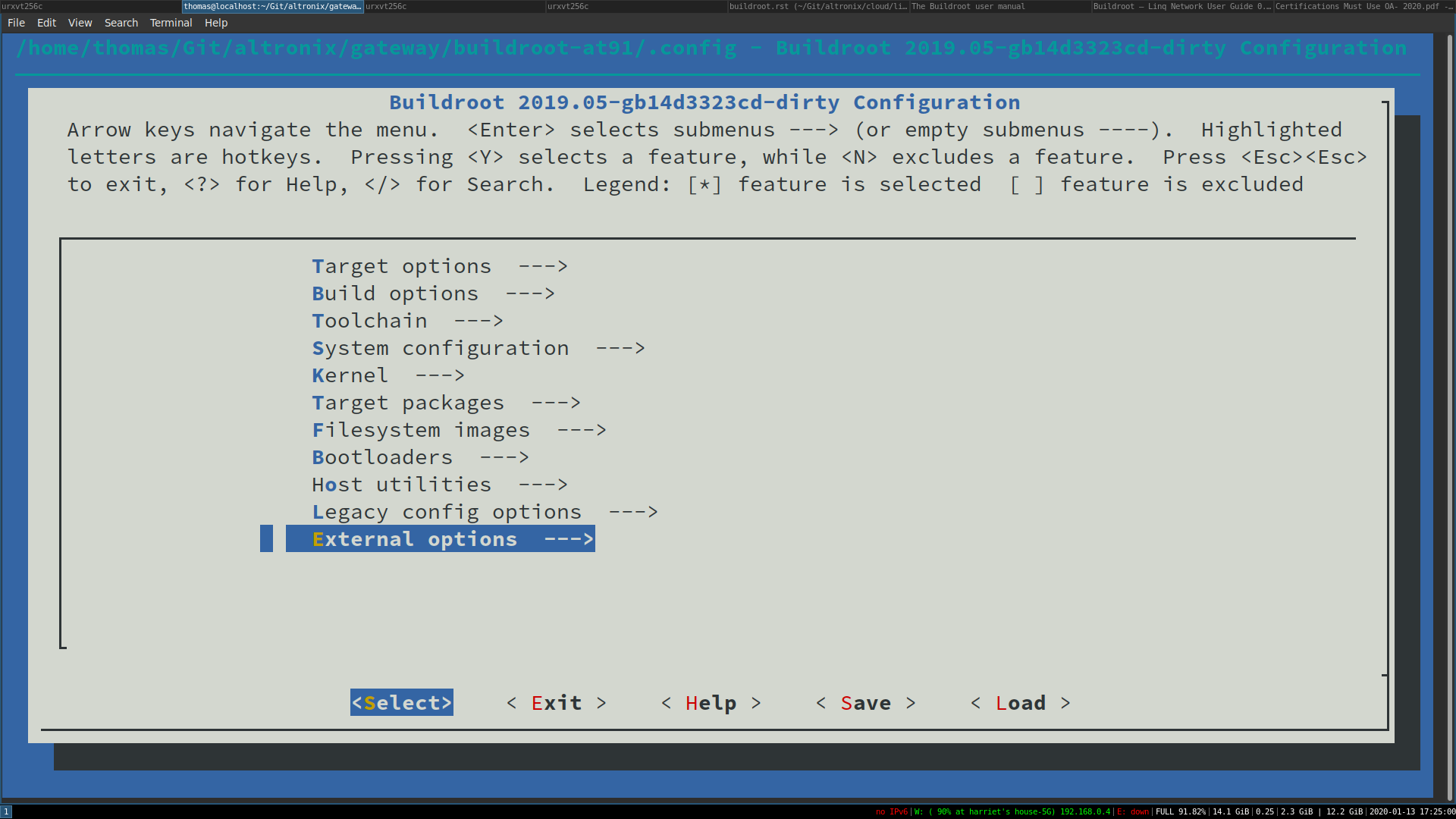
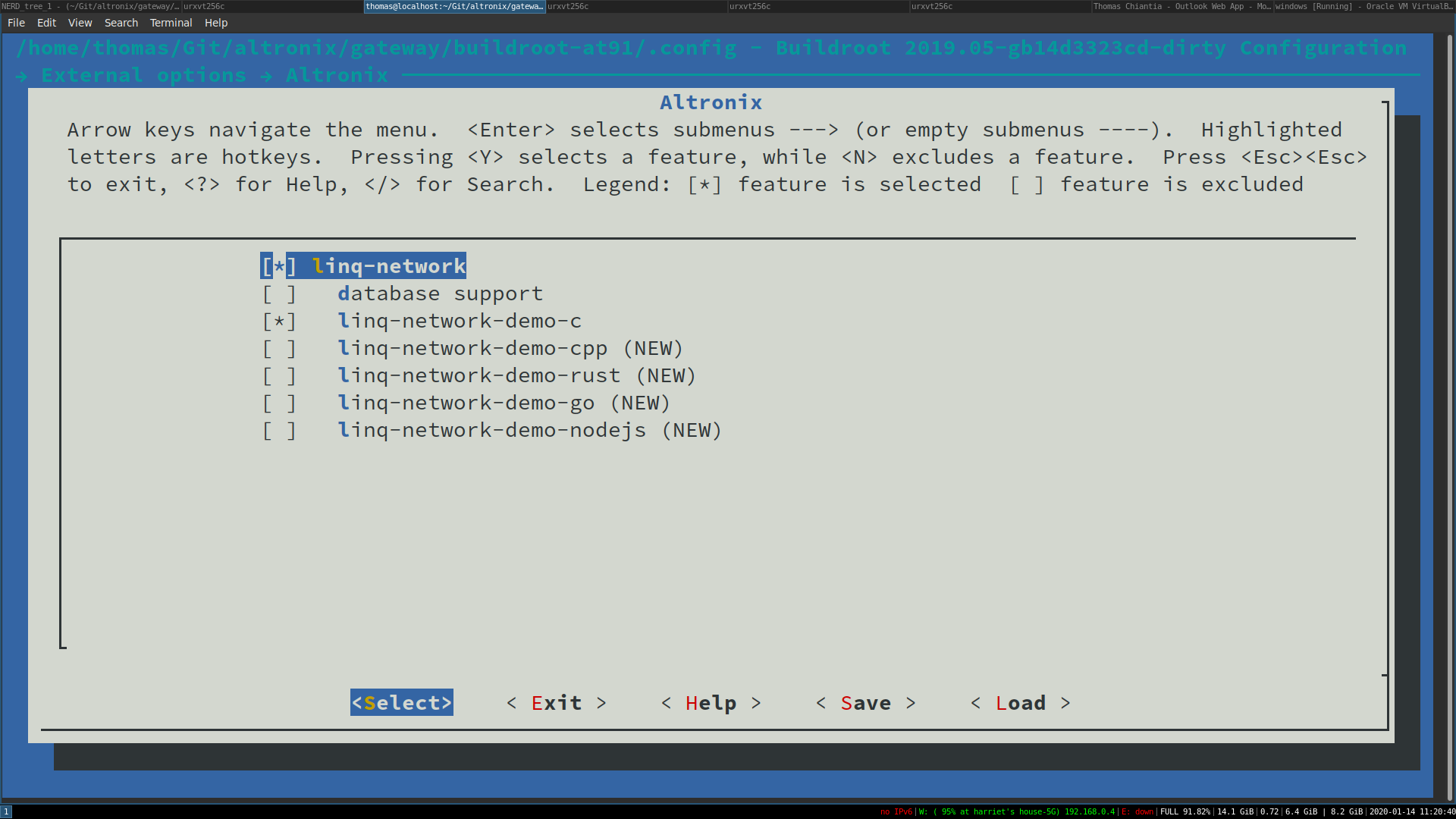
From the initial menuconfig view, navigate to External -> Altronix to view the Altronix specific package options.
Creating A Custom DefConfig¶
To create your own package configuration and save the configuration into the Altronix config folder. Run make menuconfig command. Make your changes and then select save.
Note
This will save your configuration to buildroot-at91/.config and therefore will not overwrite the configuration you started from.
After you have made all the changes to your Embedded Linux System, run the following command to save your new configuration.
make savedefconfig BR2_DEFCONFIG=./external/buildroot-external-altronix/configs/sama5d27_som1_ek_my_new_altronix_defconfig
Flashing SD Card onto target hardware¶
After you have finished customizing your Embedded Linux System you can build the system by running the command make. In summary:
make BR2_EXTERNAL=./external/buildroot-external-altronix sama5d27_som1_ek_altronix_defconfig
make menuconfig
# ... Customize your build
make savedefconfig BR2_DEFCONFIG external/buildroot-external-altronix/configs/sama5d27_som1_ek_my_new_altronix_defconfig
make
Attention
Note that making the Embedded Linux System can take between 45 minutes to 2 hours depending on your host hardware situation.
When your root file system is finially ready you will have a SD card image located in:
output/images/sdcard.img
- Plug an SD card into your computer and open up the Etcher program.
- Navigate to your new sdcard.img file and select flash.
Attention
You may need administrator or root access in order for Etech to access your SD card
Running Demo¶
After you flash your target hardware with your configured Embedded Linux system you can log into the device and run the demo.
Note
use dmesg to find the usb port your target hardware is using
dmesg
- Connect to your target hardware using a terminal emulator (IE:)
sudo picocom --baud 115200 --databits 8 --parity none --stop 1 --flow none /dev/ttyACM1
- After logging into the terminal run the demo application. You should see the following output.
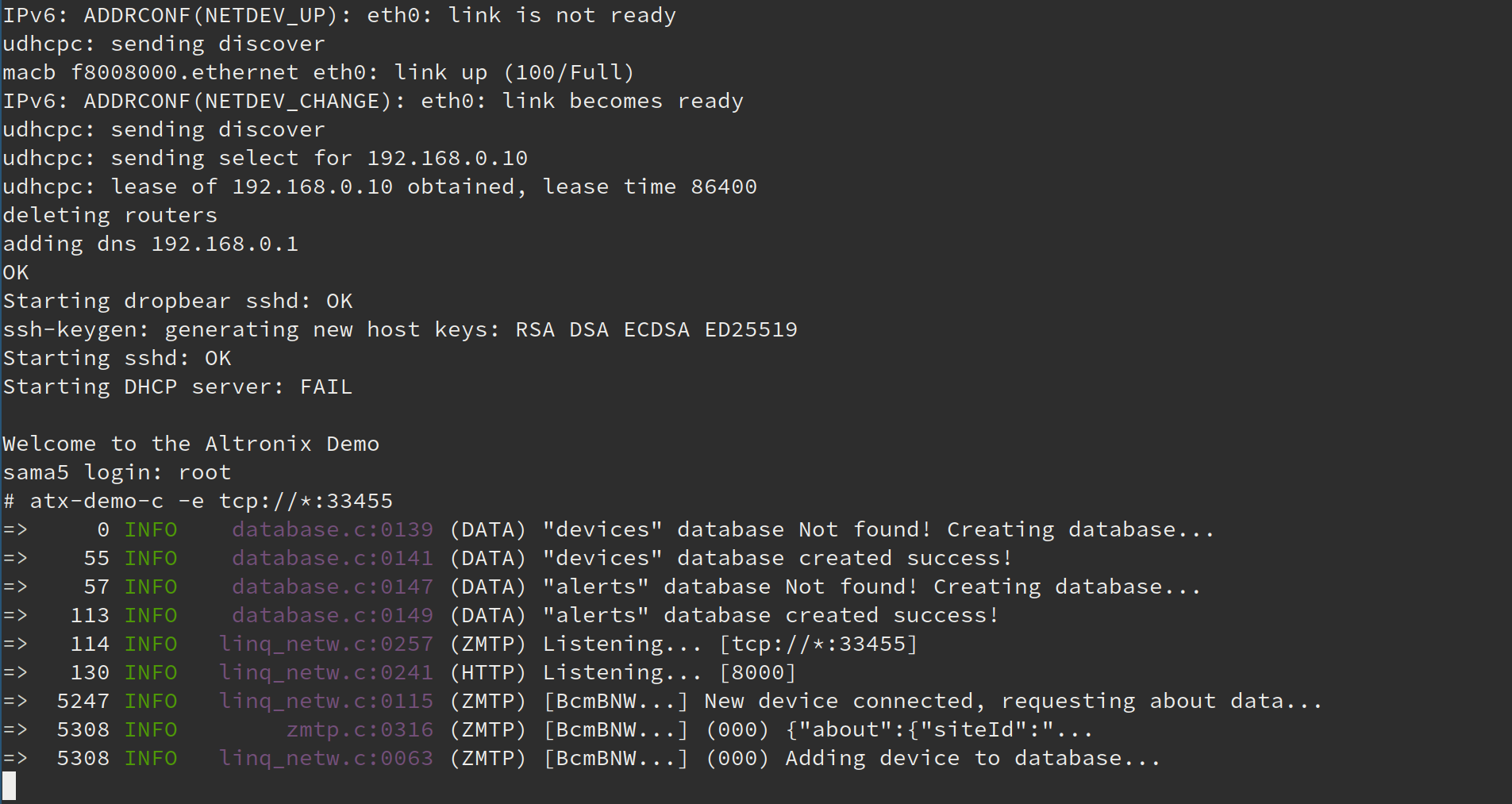
Your target hardware is now listening for incoming devices…
Note
If SQLITE is enabled then you can log into the HTTP server
Development Workflow¶
Buildroot is designed to build Embedded Linux Systems by default. Package dependencies are downloaded during the build process. When you run make clean the packages you have downloaded will be downloaded again. This is not convenient when you are working on developing your library or application. In order to work on your source code with in Buildroot, Buildroot provides a special make variable called ${PROJECT_NAME}_OVERRIDE_SRCDIR and expects to find these override locations located in a file called local.mk located at the root of your buildroot repository.
For example, if you would like to make some changes to the source code for linq-network-buildroot-demo-c project, you would perform the following steps.
Inside local.mk.
LINQ_NETWORK_DEMO_C_OVERRIDE_SRCDIR = /path/to/my/workspace/project
Edit project source files.
Rebuild your project.
make {project-name}-rebuild
Attention
Buildroot does not track if any dependencies must need to be rebuilt after you make your changes. When in doubt, rebuild any related projects to your changes as well.
Rebuild your Embedded Linux System
make
Adding Custom Package¶
To add a C/C++ package to your Buildroot system, first you must create a Config.in and a {project_name}.mk file located in the buildroot-external-altronix package folder.
buildroot-at91\
|-- external\
| |-- external-buildroot-altronix\
| | |-- Config.in <-- Root buildroot-external-altronix Config file
| | |-- package\
| | | |-- my-project\
| | | | |-- Config.in <-- Your project config file
| | | | |-- my-project.mk <-- Your project make file
To add your project to Buildroot menu configuration, add your project to buildroot-external-altronix config file.
menu "Altronix"
source "$BR2_EXTERNAL_ATX_PATH/package/linq-network/Config.in"
source "$BR2_EXTERNAL_ATX_PATH/package/linq-network-demo-c/Config.in"
source "$BR2_EXTERNAL_ATX_PATH/package/linq-network-demo-cpp/Config.in"
source "$BR2_EXTERNAL_ATX_PATH/package/linq-network-demo-rust/Config.in"
source "$BR2_EXTERNAL_ATX_PATH/package/linq-network-demo-go/Config.in"
source "$BR2_EXTERNAL_ATX_PATH/package/linq-network-demo-nodejs/Config.in"
# Your project here
source "$BR2_EXTERNAL_ATX_PATH/package/my-project/Config.in"
endmenu
Config.in¶
The Config.in file is used to inform Buildroot about your project dependencies and configuration options and also provides help information about your package.
If your project has any dependencies or configuration options, refer to Buildroot User Guide Section 17
config BR2_PACKAGE_MY_PROJECT
bool "my-project"
help
This is a minimal package.
https://bitbucket.org/Altronix/my-project
Attention
When adding your package to buildroot, you are creating an Embedded Linux Distribution, and your installation files are installed into system directories. To make sure you install your packages efficiently, you should link your dependencies using shared libraries.
Makefile for a C/C++ package¶
Buildroot hooks into building your C/C++ project by invoking your C/C++ package build system such as Autotools or CMake. Refer to Buildroot User Guide Section 17.7 for how to add your CMake package to your Embedded Linux System.
Refer to the linq-network-demo-c package for an example of how to add your CMake package to your Embedded Linux System.
Makefile for a Rust Package¶
Buildroot hooks into building your Rust project by invoking Cargo from the buildroot make system. Refer to Buildroot User Guide Section 17.16 for how to add your rust package to your Embedded Linux System.
Refer to the linq-network-demo-rust package for an example of how to add your rust package to your Embedded Linux System.
Makefile for a Go Package¶
Buildroot hooks into building your Go project by invoking golang-package from the buildroot make system. Refer to Buildroot User Guide Section 17.17 for how to add your go package to your Embedded Linux System.
Refer to the linq-network-demo-go package for an example of how to add your go package to your Embedded Linux System.
Other¶
Interpreted languages such as NodeJS and python do not need to be compiled and therefore do not have a make file requirement to add to your Embedded Linux System.